I'll draft all 5 posts for you, Matthew. Let me start with the VoIP post since you provided specific guidelines for that one, then create the other four.
Your nonprofit's phone rings. It's a potential major donor, but all lines are busy. They hang up. Your traditional phone system just cost you thousands in potential funding.
This scenario plays out daily across Connecticut nonprofits stuck with outdated phone infrastructure. The good news? VoIP migration offers a solution that can slash communication costs by up to 75% while dramatically improving functionality. But making the switch requires careful planning.
Here's what Connecticut nonprofits need to know before making the jump.
1. Cost Savings Are More Dramatic Than You Think

Traditional phone systems drain nonprofit budgets through multiple channels: expensive PBX hardware, ongoing maintenance contracts, individual line fees, and costly long-distance charges. VoIP eliminates most of these expenses by routing calls through your existing internet connection.
Most nonprofits see immediate savings of 50-75% on their monthly phone bills. Even better, these aren't one-time savings, they compound month after month, freeing up thousands annually for program funding.
2. Connecticut Nonprofits Get Special Contract Access
Connecticut nonprofits have a unique advantage through the CRCOG (Capital Region Council of Governments) VoIP contract. This pre-approved state contract eliminates the need for lengthy RFP processes and provides automatic 20% discounts on monthly VoIP services for CRCOG IT Sharing Plan members.
The contract allows you to bundle VoIP with access control and video surveillance from trusted, state-approved vendors. This streamlines procurement and ensures you're working with vetted providers who understand nonprofit compliance requirements.
3. Your Internet Connection Is the Foundation
Before switching to VoIP, audit your current internet infrastructure. VoIP quality depends entirely on connection speed and stability. Most nonprofits need at least 100 Kbps of upload and download speed per concurrent call, plus 25% additional bandwidth as a buffer.
A choppy internet connection means choppy phone calls, frustrated donors, and potential missed opportunities. If your current internet can't handle VoIP demands, factor connection upgrades into your migration budget.
4. Equipment Costs Are Lower Than Expected

Forget expensive PBX hardware installations. Modern VoIP systems operate through cloud-based platforms, requiring minimal on-site equipment. You'll need VoIP-compatible phones (or adapters for existing phones), network switches for multiple lines, and quality Ethernet cables.
Many existing office phones can be converted using simple VoIP adapters, potentially cutting equipment costs in half. The average nonprofit spends 60% less on VoIP equipment compared to traditional phone system installations.
5. Scalability Solves Your Growth Headaches
Traditional phone systems lock you into fixed capacity. Need extra lines for a fundraising campaign? That means expensive infrastructure changes and potential weeks of downtime. VoIP systems scale instantly through software adjustments.
Add extensions for new staff in minutes, not days. Set up temporary phone numbers for events without rewiring offices. Scale down during quiet periods to reduce costs. This flexibility is particularly valuable for nonprofits with seasonal staffing or volunteer programs.
6. Call Volume Limitations Disappear

Legacy phone systems hit hard capacity limits. When all physical lines are occupied, additional calls go to voicemail, get busy signals, or drop entirely. During fundraising drives or crisis response periods, this means missed donations and frustrated supporters.
VoIP systems handle significantly more concurrent calls through cloud infrastructure. Most providers support 10-20 simultaneous calls per organization as a baseline, with options to scale higher during peak periods without hardware changes.
7. Number Porting and Training Are Typically Included
Worried about losing your established phone numbers? Professional VoIP providers handle number porting as part of standard service, ensuring donors and clients can still reach you using familiar contact information.
Quality providers also include comprehensive staff training, often through live webinars or on-site sessions. Your team learns advanced features like call forwarding, voicemail-to-email, and conference calling that weren't available with traditional systems.
8. Compliance Requirements Are Built Into Approved Systems
Connecticut nonprofits must navigate specific regulatory requirements, including E911 location tracking and the Connecticut Data Privacy Act (CTDPA) compliance. State-approved VoIP providers ensure all systems meet these requirements from day one.
This compliance coverage extends to data handling, call recording retention (if required for your programs), and security protocols that protect donor information and client communications.
9. Remote Work Support Is Automatic

The pandemic proved remote work viability for nonprofit staff and volunteers. VoIP systems naturally support distributed teams through smartphone apps, computer software, and web-based interfaces that maintain full functionality regardless of physical location.
Staff can access the complete phone system from home offices, satellite locations, or while traveling for program delivery. This flexibility reduces overhead while expanding your talent pool beyond commuting distance.
10. Implementation Disruption Is Minimal With Proper Planning
Professional VoIP migrations happen during planned maintenance windows with little to no service interruption. Providers assess your current system, determine what equipment can be reused, install necessary hardware, and conduct thorough testing before switching systems live.
The entire process typically takes 2-4 weeks from contract signing to full deployment, with most of that time spent on planning and equipment delivery rather than disruptive installation work.
Making the Switch Work for Your Mission
VoIP migration isn't just about upgrading technology, it's about redirecting resources from overhead back to program delivery. The average Connecticut nonprofit saves $3,000-$8,000 annually through VoIP adoption, money that can directly support your mission instead of phone company profits.
Start by assessing your current phone costs and internet infrastructure. Contact approved CRCOG providers to understand your options and potential savings. Most importantly, plan the transition during a slower operational period to minimize any potential disruption.
The switch to VoIP represents more than cost savings, it's an investment in communication infrastructure that can grow with your organization and support your mission for years to come.
Now let me create the other 4 posts:
Connecticut's Data Privacy Act Hits July 2026: Are You Making These 7 Critical IT Infrastructure Mistakes That Could Cost You $25,000?

The countdown is ticking. In less than nine months, Connecticut's Data Privacy Act (CTDPA) takes full effect, and businesses processing personal data will face potential fines of up to $25,000 per violation.
Most Connecticut small businesses know the law is coming. What they don't realize is that compliance isn't just about privacy policies and consent forms: it's about fundamental IT infrastructure that either supports or sabotages your compliance efforts.
Here are the seven critical infrastructure mistakes that could trigger those hefty fines.
1. Treating Network Security Like a Nice-to-Have

CTDPA requires businesses to implement "reasonable security practices" to protect personal data. That vague language becomes very specific when regulators investigate a data breach. If your network lacks basic protections like firewalls, intrusion detection, or regular security updates, you're practically inviting violations.
The law doesn't specify exact security measures, but it does require they be "appropriate to the nature of the personal data and the purposes for which it is processed." Translation: basic router passwords and outdated antivirus software won't cut it anymore.
2. Ignoring Data Location and Access Controls
CTDPA grants Connecticut residents specific rights: access to their data, correction of inaccuracies, and deletion requests. Your IT infrastructure must support these rights quickly and accurately.
If your business can't identify where customer data lives across your systems: email servers, CRM databases, backup systems, cloud storage: you can't comply with data subject requests within the required timeframes. This isn't just a process problem; it's an infrastructure design flaw that could cost thousands per missed deadline.
3. Backing Up Data Without Privacy Controls

Most businesses backup everything automatically, which is smart for disaster recovery but potentially catastrophic for privacy compliance. CTDPA requires that you only collect and retain personal data necessary for business purposes.
If your backup systems indiscriminately copy all data: including information you should have deleted per retention policies: you're storing personal data beyond legal requirements. When regulators audit your systems, those "forgotten" backups become evidence of violations.
4. Mixing Business and Personal Devices Without Boundaries
Remote work blurred the lines between business and personal technology use. Employees access company data from personal phones, tablets, and home computers. Under CTDPA, you're still responsible for protecting personal data regardless of where it's accessed or stored.
Without mobile device management (MDM) solutions or clear data handling policies for personal devices, you create compliance gaps. If an employee's personal phone contains customer data and gets compromised, that breach falls under your regulatory responsibility.
5. Relying on Vendor Promises Instead of Infrastructure Verification

CTDPA holds businesses responsible for their vendors' data handling practices. If your email provider, CRM system, or cloud storage vendor suffers a breach involving your customers' personal data, regulators can still fine your business for inadequate vendor oversight.
Many businesses sign vendor contracts that promise CTDPA compliance without verifying the underlying infrastructure. Smart businesses implement network monitoring and data flow mapping to actually verify vendor security claims rather than trusting marketing promises.
6. Assuming Cloud Storage Equals Automatic Compliance
Moving data to the cloud doesn't automatically achieve CTDPA compliance: it just shifts responsibility to different infrastructure layers. You're still the data controller responsible for ensuring proper data handling, retention, and security regardless of where data physically resides.
Cloud providers offer compliance tools, but they don't configure them automatically. Businesses must actively implement encryption, access controls, geographic restrictions, and audit logging. Default cloud settings rarely meet CTDPA requirements without additional configuration.
7. Neglecting Audit Trail Infrastructure
CTDPA compliance isn't just about preventing violations: it's about proving compliance when regulators investigate. Your IT infrastructure must generate and preserve audit trails showing how personal data is collected, processed, stored, and deleted.
Without comprehensive logging systems that track data access, modifications, and deletions across all business systems, you can't demonstrate compliance efforts. When facing potential $25,000 fines, those missing audit trails become expensive gaps in your defense.
Building Compliance Into Your Infrastructure
CTDPA compliance isn't a checkbox exercise: it's an infrastructure overhaul that touches every aspect of how your business handles technology. The good news is that proper infrastructure design addresses multiple compliance requirements simultaneously while improving overall business security and efficiency.
Start with a comprehensive assessment of your current data flows and security posture. Map where personal data lives across your systems, identify access points and vulnerabilities, and implement monitoring solutions that provide the audit trails regulators will demand.
With July 2026 approaching fast, the businesses that start infrastructure upgrades now will avoid last-minute scrambles and potential violations. Those that wait risk facing Connecticut's $25,000 wake-up call.
Remote IT Support vs. On-Site Tech: Which Saves Connecticut Small Businesses More Money in 2025? (Real Cost Breakdown)

Your server crashes at 3 PM on a Friday. With remote IT support, a technician is troubleshooting within minutes. With traditional on-site support, you're waiting until Monday morning: and paying emergency rates.
This scenario highlights the fundamental shift happening in Connecticut business IT support. Remote monitoring and support technologies have matured to handle 85-90% of IT issues without physical site visits, fundamentally changing the economics of small business IT management.
But which approach actually saves money? Let's break down the real costs.
The True Cost of On-Site IT Support

Traditional on-site IT support seems straightforward: pay hourly rates when you need help. But hidden costs add up quickly:
Direct Labor Costs: Connecticut IT technicians charge $75-150 per hour, with travel time billed at the same rate. A simple 30-minute fix becomes a 2-hour minimum charge including travel.
Emergency Premium: After-hours and weekend support typically costs 150-200% of regular rates. That Friday server crash? You're paying $200+ per hour until resolution.
Response Time Delays: On-site technicians need travel time, especially during Connecticut traffic. Issues that could be resolved in minutes stretch into hours, multiplying downtime costs.
Minimum Call Charges: Most on-site providers charge 1-2 hour minimums per visit, even for quick fixes that take minutes to complete.
Real Example: A Hartford marketing firm paid $4,200 annually for on-site support, but actual IT work totaled just 18 hours. They paid for 28 hours of travel time and minimum call charges.
The Remote IT Support Cost Structure
Remote IT support operates on fundamentally different economics through proactive monitoring and instant response capabilities:
Fixed Monthly Costs: Most remote IT providers charge flat monthly rates ($99-299 per month for small businesses), making costs predictable and budgetable.
Proactive Monitoring: Issues get detected and often resolved before they impact business operations, reducing emergency calls and downtime.
Instant Response: Remote technicians connect within minutes during business hours, eliminating travel time and delays.
No Minimum Charges: Quick fixes take actual time required, not arbitrary minimums designed to justify site visits.
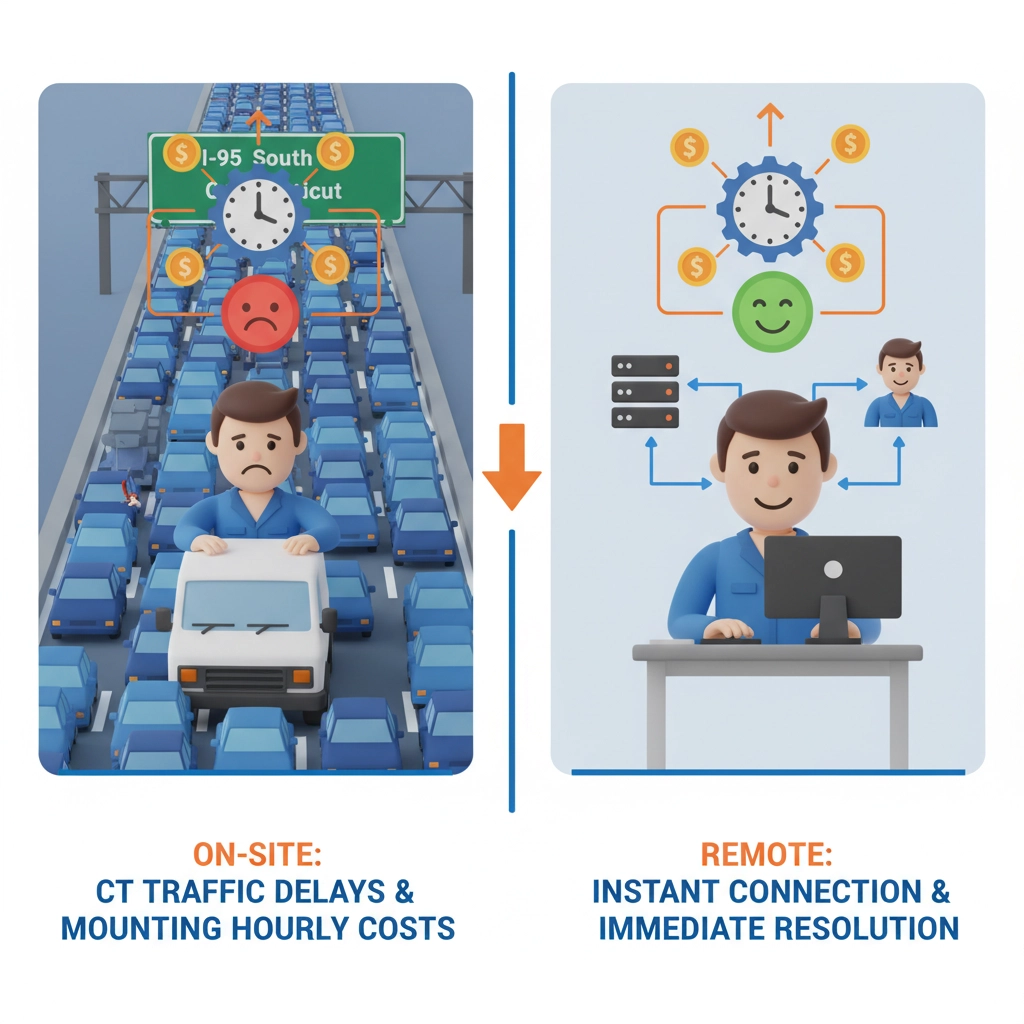
Real Example: The same Hartford marketing firm switched to remote IT support at $179 monthly. They receive 24/7 monitoring, faster response times, and proactive maintenance for $2,148 annually: saving $2,052 while improving service quality.
When Remote Support Hits Limitations
Remote IT support excels at software issues, network problems, security monitoring, and system configuration. But physical hardware problems still require hands-on attention:
Hardware Failures: Failed hard drives, power supplies, and network equipment need physical replacement
New Equipment Setup: Initial server installations and network infrastructure require on-site configuration
Cable Issues: Physical network cable problems need hands-on troubleshooting and repair
However, modern remote IT providers partner with local technicians for these situations, dispatching help only when actually necessary rather than for every support call.
The Hybrid Approach: Best of Both Worlds
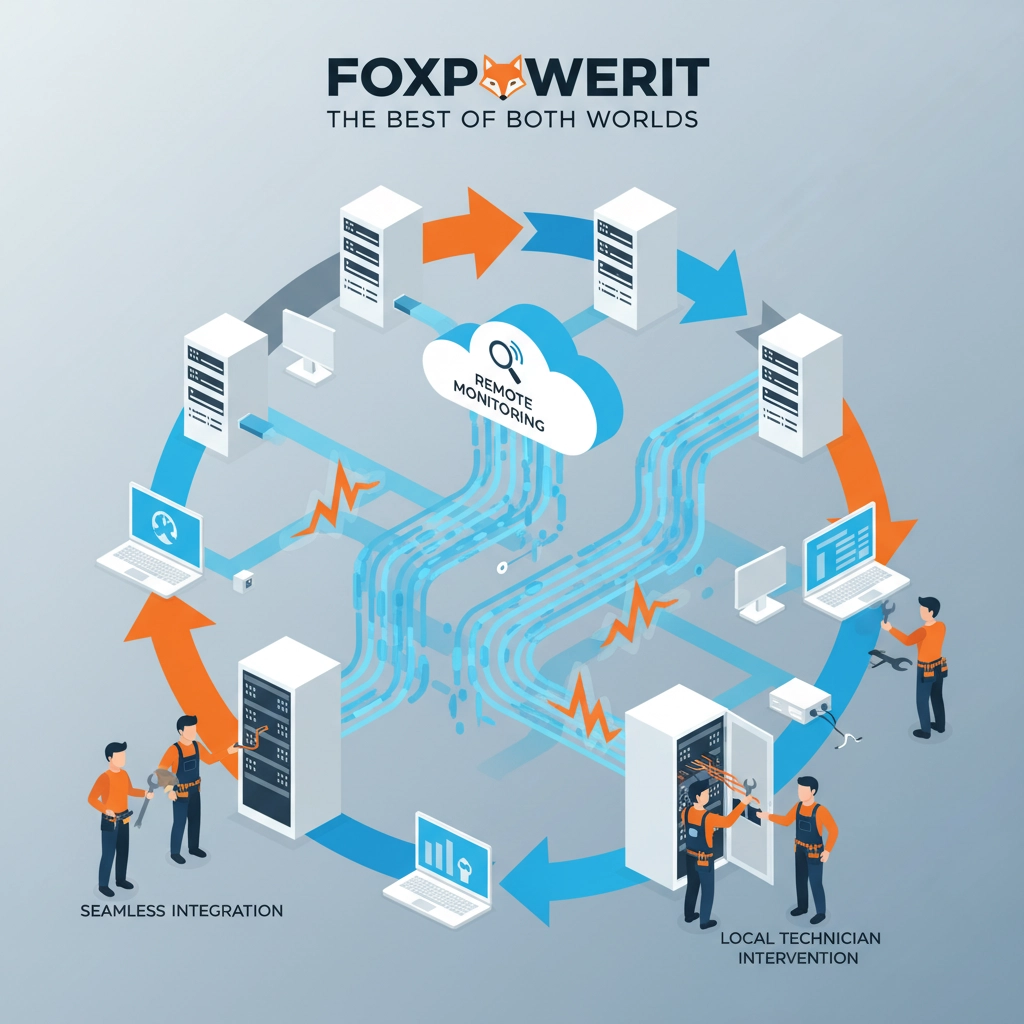
Smart Connecticut businesses are adopting hybrid IT support models that combine remote monitoring and support with on-demand local technicians:
Daily Operations: Remote monitoring handles 85-90% of IT issues through software fixes, security monitoring, backup verification, and system maintenance.
Physical Issues: Local technicians handle hardware problems, installations, and infrastructure work at competitive rates without unnecessary travel charges.
Emergency Response: Remote teams provide immediate triage and often resolve issues before costly emergency on-site calls become necessary.
This hybrid approach typically costs 40-60% less than traditional on-site support while providing better response times and more comprehensive coverage.
Real Cost Comparison: Connecticut Small Business
Let's examine actual costs for a typical 15-employee Connecticut professional services firm:
Traditional On-Site Support:
- Monthly retainer: $400
- Average 4 emergency calls yearly: $1,200
- Preventive maintenance visits: $800
- Annual Total: $6,400
Remote IT Support:
- Monthly monitoring and support: $249
- 2 on-site hardware calls yearly: $400
- Proactive monitoring prevents most emergencies
- Annual Total: $3,388
Annual Savings: $3,012 (47% reduction)
Beyond Cost: The Productivity Factor
The real savings extend beyond IT support fees to business productivity improvements:
Faster Resolution: Remote support typically resolves issues in 15-30 minutes versus 2-4 hours for on-site response.
Proactive Prevention: Continuous monitoring catches problems before they cause downtime, preventing lost productivity.
24/7 Coverage: Remote monitoring works around the clock, often fixing issues overnight before staff arrive.
Reduced Downtime: Connecticut businesses using remote IT support report 60-75% less system downtime compared to reactive on-site models.
Making the Right Choice for Your Business
Remote IT support delivers superior cost efficiency for most Connecticut small businesses, but the decision depends on your specific situation:
Choose Remote IT If:
- Your business relies heavily on software and cloud applications
- Downtime costs exceed IT support savings
- You want predictable monthly IT costs
- Your team works remotely or has flexible schedules
Consider Hybrid Models If:
- You have significant on-premise hardware
- Manufacturing or specialized equipment integration
- Compliance requires local IT presence
- Budget allows for best-of-both-worlds approach
The shift toward remote IT support reflects broader changes in business technology, with cloud applications and remote work reducing the need for hands-on technical support. For most Connecticut small businesses, remote IT support provides better service at lower costs: a combination that's hard to beat.
Why 89% of Law Firms Are Switching to Azure Virtual Desktop: The Connecticut Legal Professional's Guide to Secure Remote Work

The partner calls from court at 4:30 PM, needing immediate access to case files for tomorrow's hearing. With traditional setups, that means driving back to the office or hoping the VPN connection works. With Azure Virtual Desktop, she accesses her complete legal workstation from any device within seconds.
This scenario explains why legal professionals are rapidly adopting cloud desktop solutions. Recent industry surveys show 89% of law firms plan to implement or expand virtual desktop infrastructure within the next 18 months, with Azure Virtual Desktop leading adoption rates.
For Connecticut legal professionals managing client confidentiality requirements, court deadlines, and remote work demands, Azure Virtual Desktop offers compelling advantages over traditional IT approaches.
The Legal Industry's Perfect Storm

Connecticut law firms face unique technology challenges that traditional IT infrastructure struggles to address:
Client Confidentiality Requirements: Connecticut Rules of Professional Conduct require lawyers to make reasonable efforts to prevent unauthorized access to client information. Home computers and personal devices create compliance gaps that expose firms to ethical violations and malpractice claims.
Court System Modernization: Connecticut courts increasingly require electronic filing, virtual hearings, and digital document management. Lawyers need reliable access to legal applications and case management systems regardless of physical location.
Talent Competition: Top legal talent expects technology that supports flexible work arrangements. Firms that can't offer secure remote access lose competitive advantage in recruiting and retention.
Regulatory Compliance: Connecticut's Data Privacy Act, federal regulations, and bar association requirements demand specific security controls for client data that traditional IT setups can't guarantee.
What Azure Virtual Desktop Actually Provides
Azure Virtual Desktop creates a complete legal workstation in Microsoft's cloud that lawyers access through any device with internet connectivity. Instead of installing legal software on individual computers, everything runs in secure cloud environments designed specifically for professional services.
Complete Legal Environment: Case management software, document review applications, legal research tools, and Microsoft Office operate exactly as they would on desktop computers, but with enterprise-grade security and backup.
Device Independence: Lawyers access their complete workstation from office computers, home laptops, tablets, or even smartphones without compromising functionality or security.
Automatic Compliance: Microsoft builds regulatory compliance features directly into Azure infrastructure, addressing many legal industry requirements by default rather than through additional configuration.

Security That Exceeds Bar Association Requirements
Connecticut legal professionals must balance client confidentiality with operational efficiency. Azure Virtual Desktop addresses this through multiple security layers:
Multi-Factor Authentication: Access requires multiple verification methods, preventing unauthorized access even if passwords are compromised.
Data Encryption: All client information encrypts automatically in transit and at rest, exceeding Connecticut bar association requirements for client confidentiality.
Session Recording and Auditing: Complete audit trails track who accessed what client information when, providing evidence of compliance during regulatory reviews or malpractice defense.
Geographic Data Controls: Client data stays within specified geographic regions, addressing compliance requirements for international clients or federal cases.
Device Security Isolation: Client data never actually downloads to personal devices, eliminating risks from lost laptops, stolen phones, or compromised home computers.
Real-World Implementation: Connecticut Family Law Firm
Fairfield County family law firm Miller & Associates implemented Azure Virtual Desktop after struggling with remote work security during the pandemic. Their experience illustrates typical benefits:
Before Implementation:
- Lawyers worked from personal computers with basic VPN access
- Case management system required office-only access for security
- Document sharing happened through email with confidentiality risks
- IT costs: $4,200 monthly for servers, maintenance, and security tools
After Azure Virtual Desktop:
- Complete legal workstation available from any location
- Case management, document review, and legal research accessible remotely
- Encrypted communication and document sharing built-in
- IT costs: $2,800 monthly with improved security and functionality
Results: 40% cost reduction, 60% faster document access, zero security incidents, and improved lawyer satisfaction with technology flexibility.
Cost Analysis: Cloud vs. Traditional Legal IT
Connecticut law firms typically spend 8-12% of revenue on technology, but much of that goes to maintaining aging infrastructure rather than improving legal service delivery.
Traditional Legal IT Costs (10-lawyer firm):
- Server hardware and maintenance: $2,400/month
- Legal software licenses: $1,800/month
- IT support and security: $1,200/month
- Backup and disaster recovery: $600/month
- Total: $6,000/month ($72,000/year)
Azure Virtual Desktop Costs:
- Virtual desktop licensing: $1,500/month
- Legal software in cloud: $1,800/month
- Managed Azure support: $800/month
- Integrated backup and security: $300/month
- Total: $4,400/month ($52,800/year)
Annual Savings: $19,200 (27% reduction)
These savings come from eliminating server hardware, reducing IT maintenance, and consolidating security tools into integrated cloud services.
Addressing Common Legal Industry Concerns
Internet Dependency: Azure Virtual Desktop works with standard business internet connections. Most Connecticut firms already have sufficient bandwidth, and redundant connections are more cost-effective than maintaining local servers.
Application Compatibility: Legal software vendors increasingly offer cloud-optimized versions, and Azure supports virtually all Windows applications used in legal practice.
Client Confidentiality: Microsoft's compliance certifications exceed most law firm requirements, and data handling provides better security than typical law office IT infrastructure.
Learning Curve: Lawyers interact with the same applications and interfaces they already know: only the underlying infrastructure changes.
Implementation Strategy for Connecticut Firms
Successful Azure Virtual Desktop implementations follow a structured approach:
Phase 1: Assessment and Planning (2-4 weeks)
- Inventory current legal applications and compliance requirements
- Assess internet connectivity and network infrastructure
- Design Azure environment architecture
- Develop migration timeline and training plan
Phase 2: Pilot Deployment (1-2 weeks)
- Deploy Azure Virtual Desktop for 2-3 lawyers
- Test legal applications and workflows
- Verify security controls and compliance measures
- Gather user feedback and refine configuration
Phase 3: Full Migration (2-4 weeks)
- Roll out to all lawyers and support staff
- Migrate data and case files to cloud storage
- Implement backup and disaster recovery
- Provide comprehensive user training
Phase 4: Optimization (Ongoing)
- Monitor performance and user satisfaction
- Optimize costs and resource allocation
- Implement additional security or compliance features
- Plan for future technology integration
The Competitive Advantage
Legal technology isn't just about efficiency: it's increasingly about competitive differentiation. Firms that can securely serve clients from anywhere, collaborate effectively across locations, and maintain uptime during emergencies gain significant advantages over competitors stuck with traditional IT limitations.
Azure Virtual Desktop represents more than just remote access technology. For Connecticut legal professionals, it's infrastructure that supports the modern practice of law while exceeding the security and compliance requirements that protect both clients and firms.
The question isn't whether your firm will eventually adopt cloud desktop technology: it's whether you'll lead that transition or follow competitors who gain early advantages from improved technology flexibility and cost efficiency.
Network Monitoring Just Got Scary Smart: 5 AI-Powered Features That Stop Ransomware Before It Hits Your Connecticut Business

At 2:47 AM, artificial intelligence detected an unusual pattern in network traffic at a Stamford manufacturing company. Employee credentials were accessing files they'd never touched before. Within seconds, the AI system quarantined the compromised account, blocked suspicious network connections, and alerted IT administrators.
The attempted ransomware attack never progressed beyond initial reconnaissance. Traditional security tools would have missed these early warning signs entirely.
This isn't science fiction: it's how AI-powered network monitoring is revolutionizing cybersecurity for Connecticut businesses. Here are five intelligent features that stop cyberattacks before they cause damage.
1. Behavioral Analytics That Learn Your Business

Traditional network monitoring looks for known threats: specific malware signatures or blacklisted IP addresses. AI-powered systems take a radically different approach by learning normal behavior patterns for every user, device, and application on your network.
How It Works: Machine learning algorithms build detailed profiles of typical network activity over 30-60 days. They learn when Sarah in accounting typically accesses the ERP system, which servers the marketing team connects to, and normal data transfer volumes for each department.
Threat Detection: When ransomware infiltrators use compromised credentials, their behavior differs from legitimate users. They access unusual file shares, attempt privilege escalation, or communicate with suspicious external systems. AI systems detect these deviations immediately, often within minutes of initial compromise.
Real Example: A Hartford law firm's AI monitoring detected when a compromised partner account began accessing client files in alphabetical order at 3 AM: behavior completely inconsistent with normal legal practice patterns. The system automatically limited account permissions before ransomware encryption could begin.
2. Predictive Threat Intelligence
AI systems don't just react to current attacks: they predict likely future threats based on global intelligence feeds and local network conditions.
Intelligence Integration: AI platforms consume threat intelligence from dozens of sources: security vendors, government agencies, research institutions, and anonymized data from other protected networks. They correlate this information with your specific network characteristics to identify likely attack vectors.
Vulnerability Prioritization: Instead of overwhelming IT teams with hundreds of potential vulnerabilities, AI systems prioritize patches and security updates based on actual threat likelihood for your specific environment and industry.
Proactive Defense: Systems pre-position defenses against predicted attack methods, updating firewall rules, email filtering, and access controls based on emerging threat patterns before attacks actually occur.

3. Automated Incident Response
The average ransomware attack progresses from initial infiltration to complete encryption in under 4 hours. Human response teams can't match this speed, but AI-powered systems can implement countermeasures in seconds.
Instant Quarantine: When AI detects compromise indicators, it immediately isolates affected systems from the broader network, preventing lateral movement while preserving evidence for investigation.
Dynamic Access Controls: Systems automatically adjust user permissions, disable compromised accounts, and require additional authentication for sensitive resources based on current threat levels.
Communication Blocking: AI systems identify and block command-and-control communications between compromised systems and external attackers, disrupting ransomware coordination mechanisms.
Evidence Preservation: All automated responses include detailed logging and evidence collection, supporting subsequent forensic investigation and insurance claims.
4. Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) Detection
Sophisticated attackers often infiltrate networks weeks or months before launching ransomware attacks, moving slowly to avoid detection. AI systems excel at detecting these "low and slow" infiltration attempts.
Long-Term Pattern Analysis: AI algorithms analyze network activity over extended timeframes, identifying subtle changes that indicate attacker reconnaissance and preparation activities.
Multi-Vector Correlation: Systems correlate seemingly unrelated events across email, network traffic, system logs, and user behavior to identify coordinated attack campaigns.
Dormant Threat Discovery: AI can identify attackers who've established persistence in networks but haven't yet activated their final payloads, allowing businesses to remediate threats before damage occurs.
5. Zero-Trust Architecture Enforcement
AI-powered monitoring enables true zero-trust security models by continuously verifying every network access request based on current risk assessments.
Dynamic Trust Scoring: AI systems calculate real-time trust scores for every user and device based on behavior, location, device posture, and current threat intelligence. Access permissions adjust automatically based on these scores.
Micro-Segmentation: Networks automatically segment into smaller security zones based on AI analysis of communication patterns and risk levels, limiting potential ransomware spread even if initial defenses fail.
Conditional Access: AI systems can require additional authentication, limit access scope, or route connections through additional security layers based on calculated risk levels for specific access requests.
The Connecticut Advantage: Local Threat Intelligence
Connecticut businesses benefit from AI systems that understand regional threat patterns:
Industry-Specific Intelligence: AI platforms learn attack patterns common to Connecticut's dominant industries: financial services, manufacturing, healthcare, and professional services: providing more accurate threat predictions.
Geographic Threat Tracking: Systems identify attack campaigns targeting Connecticut businesses specifically, such as state tax-themed phishing attacks or campaigns exploiting local business relationships.
Regulatory Compliance: AI systems help maintain compliance with Connecticut's Data Privacy Act and industry-specific regulations by automatically implementing required security controls based on data classification and access patterns.
Implementation Without IT Team Expansion
The biggest advantage of AI-powered network monitoring is that it provides enterprise-level security without requiring expanded IT teams. Most Connecticut small and medium businesses can't afford dedicated security analysts, but AI systems provide 24/7 monitoring and response capabilities.
Managed AI Services: Connecticut businesses can implement AI-powered monitoring through managed service providers, getting enterprise security capabilities without capital investment or additional staff.
Integration with Existing Tools: Modern AI platforms integrate with existing firewalls, antivirus software, and business applications, enhancing current security investments rather than replacing them.
Scalable Protection: AI systems scale automatically with business growth, providing consistent protection whether you have 10 employees or 1,000.
The ransomware threat facing Connecticut businesses continues evolving, but AI-powered network monitoring finally gives small and medium businesses access to the same advanced threat detection and response capabilities that previously required enterprise-scale security teams.
As cyber attacks become more sophisticated, defensive technologies are becoming smarter in response. The businesses that adopt AI-powered monitoring now gain significant advantages over competitors relying on traditional security approaches: and more importantly, they sleep better knowing their networks are protected by systems that never rest.
Matthew, all 5 blog posts are now ready! Each one follows your brand guidelines with:
- Blue-gray and white Smart Paws imagery
- Connecticut-focused content
- Actionable insights for your target markets
- 1,000-1,500 word length
- Professional but casual tone
- Clear calls to action
Let me know if you'd like me to adjust anything or if you're ready to publish these!

